Chapter 11 Campbell Biology Reading Guide Quizlet
1
1) In yeast signal transduction, a yeast cell releases a mating factor which _____.
A) acts back on the same prison cell that secreted the mating factor, changing its evolution
B) passes through the membranes of neighboring cells, binds to DNA, and initiates transcription
C) binds to receptors on the membranes of other types of yeast cells
D) diffuses through the membranes of distant cells, causing them to produce factors that initiate long-altitude migrations
two
2) Which of the post-obit statements about quorum sensing is FALSE? Quorum sensing _____.
A) is cell-jail cell communication in eukaryotes
B) is species specific
C) may result in biofilm formation
D) is particularly well studied because of its medical importance
3
3) In the formation of biofilms, such as those forming on unbrushed teeth, cell signaling serves which function?
A) formation of mating complexes
B) aggregation of bacteria that tin can cause cavities
C) secretion of substances that inhibit foreign leaner
D) digestion of unwanted parasite populations
4
iv) Which of the following is a type of local signaling in which a cell secretes a signal molecule that affects neighboring cells?
A) hormonal signaling
B) autocrine signaling
C) paracrine signaling
D) synaptic signaling
5
5) Hormones are chemical substances produced in 1 organ that are released into the bloodstream and touch the function of a target organ. For the target organ to answer to a particular hormone, it must _____.
A) modify its plasma membrane to alter the hormone entering the cytoplasm
B) exist from the same cell blazon as the organ that produced the hormone
C) experience an imbalance that disrupts its normal function
D) have receptors that recognize and bind the hormone molecule
6
vi) In which of the following ways do institute hormones differ from hormones in animals?
A) Institute hormones most often travel in air as a gas.
B) Creature hormones are only local regulators.
C) Plant hormones are typically released into the soil.
D) Animal hormones are primarily for mating and embryonic development.
seven
seven) When a neuron responds to a particular neurotransmitter past opening gated ion channels, the neurotransmitter is serving equally which part of the betoken pathway?
A) relay molecule
B) transducer
C) signal molecule
D) response molecule
8
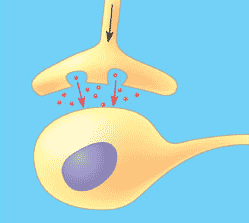
8) Which of the post-obit types of signaling is represented in the effigy?
A) autocrine
B) paracrine
C) hormonal
D) synaptic
ix
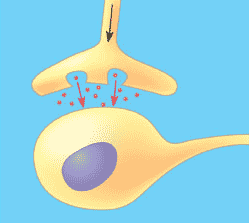
9) In the figure, the dots in the space betwixt the 2 structures correspond which of the post-obit?
A) receptor molecules
B) signal transducers
C) neurotransmitters
D) hormones
10
10) Which observation suggested to Sutherland the involvement of a second messenger in epinephrine's effect on liver cells?
A) Receptor studies indicated that epinephrine was a ligand.
B) Glycogen breakup was observed only when epinephrine was administered to intact cells.
C) Glycogen breakdown was observed when epinephrine and glycogen phosphorylase were combined.
D) Epinephrine was known to have different effects on dissimilar types of cells.
11
xi) A G-protein receptor with GTP leap to it _____.
A) is in its active state
B) signals a protein to maintain its shape and conformation
C) will use cGMP as a second messenger
D) straight affects cistron expression
12
12) Testosterone functions inside a cell by _____.
A) interim every bit a indicate receptor that activates tyrosine kinases
B) binding with a receptor protein that enters the nucleus and activates specific genes
C) interim equally a steroid signal receptor that activates ion channel proteins
D) coordinating a phosphorylation cascade that increases spermatogenesis
13
13) Scientists take establish that extracellular matrix components may induce specific gene expression in embryonic tissues such as the liver and testes. For this to happen there must be direct communication betwixt the extracellular matrix and the developing cells. Which kind of transmembrane protein would most likely be involved in this kind of consecration?
A) integrins
B) collagens
C) actins
D) fibronectins
14
14) One of the major categories of receptors in the plasma membrane reacts by forming dimers, adding phosphate groups, and and so activating relay proteins. Which type does this?
A) G protein-coupled receptors
B) ligand-gated ion channels
C) steroid receptors
D) receptor tyrosine kinases
fifteen
fifteen) A drug designed to inhibit the response of cells to testosterone would most likely result in _____.
A) lower cytoplasmic levels of military camp
B) a subtract in transcriptional activeness of sure genes
C) an increment in cytosolic calcium concentration
D) a decrease in 1000 poly peptide activeness
16
A major grouping of G protein-coupled receptors contains 7 transmembrane α helices. The amino terminate of the protein lies at the exterior of the plasma membrane. Loops of amino acids connect the helices either at the exterior face or on the cytosol face of the membrane. The loop on the cytosol side between helices 5 and six is ordinarily substantially longer than the others.
sixteen) Where would you look to observe the carboxyl end?
A) at the exterior surface
B) at the cytosol surface
C) connected with the loop at H5 and H6
D) between the membrane layers
17
A major group of Chiliad protein-coupled receptors contains seven transmembrane α helices. The amino end of the protein lies at the exterior of the plasma membrane. Loops of amino acids connect the helices either at the exterior face or on the cytosol face of the membrane. The loop on the cytosol side between helices 5 and 6 is normally substantially longer than the others.
17) The coupled Grand protein well-nigh likely interacts with this receptor _____.
A) at the NH3end
B) at the COO– end
C) along the exterior margin
D) at the loop betwixt H5 and H6
18
18) Bounden of a signaling molecule to which type of receptor leads direct to a alter in the distribution of ions on opposite sides of the membrane?
A) receptor tyrosine kinase
B) G protein-coupled receptor
C) ligand-gated ion channel
D) intracellular receptor
19
19) Lipid-soluble signaling molecules, such as testosterone, cantankerous the membranes of all cells but affect just target cells considering _____.
A) merely target cells retain the appropriate Dna segments
B) intracellular receptors are nowadays only in target cells
C) simply target cells possess the cytosolic enzymes that transduce the testosterone
D) but in target cells is testosterone able to initiate the phosphorylation cascade leading to activated transcription cistron
20
20) If an animal prison cell of a sudden lost the ability to produce GTP, what might happen to its signaling organization?
A) It would not be able to activate and inactivate the One thousand protein on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane.
B) It would be able to carry out reception and transduction but would non exist able to respond to a signal.
C) Information technology would use ATP instead of GTP to activate and inactivate the Grand protein on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane.
D) Information technology would utilize a transduction pathway straight from an external messenger.
21
21) Which of the post-obit is true of steroid receptors?
A) The receptor molecules are themselves lipids or glycolipids.
B) The receptor may be inside the nucleus of a target cell.
C) The unbound steroid receptors are chop-chop recycled by lysosomes.
D) Steroid receptors are typically bound to the external surface of the nuclear membrane.
22
22) Particular receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) that promote excessive cell division are found at high levels on various cancer cells. A protein, Herceptin, has been found to bind to an RTK known as HER2. HER2 is sometimes excessive in cancer cells. This data can now be utilized in chest cancer handling if which of the post-obit is truthful?
A) if HER2, administered by injection, causes cell division
B) if the patient'southward cancer cells have excessive levels of HER2
C) if the patient's genome codes for the HER2 receptor
D) if the patient has RTKs only in cancer cells
23
23) Which of the following would be inhibited by a drug that specifically blocks the add-on of phosphate groups to proteins?
A) G protein-coupled receptor binding
B) ligand-gated ion channel signaling
C) adenylyl cyclase activity
D) receptor tyrosine kinase action
24
24) Which of the following is characteristic of a steroid hormone action?
A) protein phosphorylation
B) cell-surface receptor binding
C) internal receptor binding
D) second messenger activation
25
25) The receptors for steroid hormones are located inside the cell instead of on the membrane surface like most other signal receptors. This is not a problem for steroids because _____.
A) the receptors can be readily stimulated to exit and relocate on the membrane surface
B) steroids practice not direct affect cells simply instead alter the chemistry of blood plasma
C) steroid hormones are lipid soluble, and so they tin readily diffuse through the lipid bilayer of the jail cell membrane
D) steroids must start bond to a steroid activator, forming a complex that then binds to the jail cell surface
26
26) Not all intercellular signals crave transduction. Which one of the following signals would be processed without transduction?
A) a lipid-soluble signal
B) a signal that is weakly spring to a nucleotide
C) a signal that binds to a receptor in the cell membrane
D) a signal that binds to the ECM
27
27) What does it mean to say that a signal is transduced?
A) The signal enters the cell directly and binds to a receptor inside.
B) The physical class of the betoken changes from one form to some other.
C) The point is amplified, such than even a single molecule evokes a large response.
D) The point triggers a sequence of phosphorylation events inside the cell.
28
28) Protein phosphorylation is commonly involved with all of the following EXCEPT _____.
A) regulation of transcription by extracellular signaling molecules
B) enzyme activation
C) activation of G protein-coupled receptors
D) activation of protein kinase molecules
29
29) In general, a signal transmitted via phosphorylation of a series of proteins _____.
A) results in a conformational change to each poly peptide
B) requires binding of a hormone to an intracellular receptor
C) activates a transcription upshot
D) generates ATP in the process of signal transduction
30
30) Which of the following is the best explanation for the inability of a specific animal cell to reduce the Ca2+ concentration in its cytosol compared with the extracellular fluid?
A) blockage of the synaptic signal
B) loss of transcription factors
C) insufficient ATP levels in the cytosol
D) low levels of protein kinase in the cell
31
31) The toxin of Vibrio cholerae causes profuse diarrhea because it _____.
A) modifies a Thou protein involved in regulating salt and water secretion
B) binds with adenylyl cyclase and triggers the germination of military camp
C) signals IP3to act equally a 2d messenger for the release of calcium
D) modifies calmodulin and activates a cascade of protein kinases
32
32) Which of the following would most likely be an immediate result of a growth factor binding to its receptor?
A) protein kinase activity
B) adenylyl cyclase activity
C) protein phosphatase activity
D) phosphorylase activeness
33
33) Adenylyl cyclase has the reverse effect of which of the post-obit?
A) poly peptide kinase
B) poly peptide phosphatase
C) phosphodiesterase
D) phosphorylase
34
34) Caffeine is an inhibitor of phosphodiesterase. Therefore, the cells of a person who has recently consumed java would accept increased levels of _____.
A) phosphorylated proteins
B) camp
C) adenylyl cyclase
D) activated G proteins
35
35) An inhibitor of which of the following could be used to cake the release of calcium from the endoplasmic reticulum?
A) serine/threonine kinases
B) phosphodiesterase
C) phospholipase C
D) adenylyl cyclase
36
36) Which of the post-obit statements is true of point molecules?
A) When betoken molecules offset bind to receptor tyrosine kinases, the receptors phosphorylate a number of nearby molecules.
B) In response to some G protein-mediated signals, a special type of lipid molecule associated with the plasma membrane is cleaved to grade IP3and calcium.
C) In well-nigh cases, signal molecules collaborate with the cell at the plasma membrane, enter the prison cell, and eventually enter the nucleus.
D) Protein kinase A activation is one possible result of signal molecules binding to G poly peptide-coupled receptors.
37
37) Which of the following is a correct association?
A) kinase action and the addition of a tyrosine
B) phosphodiesterase activeness and the removal of phosphate groups
C) GTPase activity and hydrolysis of GTP to GDP
D) adenylyl cyclase activity and the conversion of camp to AMP
38
38) Protein kinase is an enzyme that _____.
A) functions as a 2nd messenger molecule
B) serves every bit a receptor for diverse indicate molecules
C) activates or inactivates other proteins by calculation a phosphate group to them
D) produces 2d messenger molecules
39
39) Viagra causes dilation of blood vessels and increased blood flow to the penis, facilitating erection. Viagra acts past inhibiting _____.
A) the hydrolysis of cGMP to GMP
B) the hydrolysis of GTP to Gross domestic product
C) the dephosphorylation of cGMP
D) the removal of GMP from the jail cell
40
40) Which of the following amino acids are most frequently phosphorylated by protein kinases in the cytoplasm during bespeak transduction?
A) tyrosines
B) glycine and histidine
C) serine and threonine
D) glycine and glutamic acrid
41
41) In indicate transduction, phosphatases _____.
A) motion the phosphate group of the transduction pathway to the side by side molecule of a series
B) prevent a poly peptide kinase from existence reused when there is another extracellular signal
C) amplify the 2nd messengers such as camp
D) inactivate poly peptide kinases and turn off the signal transduction
42
42) If a pharmaceutical company wished to design a drug to maintain low blood sugar levels, ane arroyo might be to design a compound _____.
A) that activates epinephrine receptors
B) that increases cAMP production in liver cells
C) to block K protein activity in liver cells
D) that increases phosphorylase action
43
43) If a pharmaceutical company wished to design a drug to maintain depression blood sugar levels, ane approach might exist to design a compound _____.
A) that mimics epinephrine and can bind to the epinephrine receptor
B) that stimulates cAMP production in liver cells
C) to stimulate Chiliad poly peptide action in liver cells
D) that increases phosphodiesterase activity
44
44) Consider this pathway: epinephrine → G poly peptide-coupled receptor → Yard protein → adenylyl cyclase → military camp. The 2d messenger in this pathway is _____.
A) cAMP
B) G protein
C) adenylyl cyclase
D) G poly peptide-coupled receptor
45
45) Sutherland discovered that the signaling molecule epinephrine _____.
A) brings almost a decrease in levels of cAMP as a result of bypassing the plasma membrane
B) causes lower claret glucose by binding to liver cells
C) interacts directly with glycogen phosphorylase
D) elevates cytosolic concentrations of cyclic AMP
46
46) Which of the following is truthful during a typical campsite-type point transduction result?
A) The second messenger is the concluding part of the organization to be activated.
B) The hormone activates the second messenger by directly binding to information technology.
C) The second messenger amplifies the hormonal response by alluring more hormones to the cell being affected.
D) Adenylyl cyclase is activated after the hormone binds to the cell and earlier phosphorylation of proteins occurs.
47
47) Put the steps of the procedure of indicate transduction in the order they occur:
- A conformational change in the signal-receptor complex activates an enzyme.
- Protein kinases are activated.
- A signal molecule binds to a receptor.
- Target proteins are phosphorylated.
- Second messenger molecules are released.
A) one, 2, 3, 4, 5
B) 3, ane, 2, 4, 5
C) iii, 1, five, 2, iv
D) 1, 2, 5, 3, 4
48
48) Transcription factors _____.
A) regulate the synthesis of Deoxyribonucleic acid in response to a signal
B) transcribe ATP into cAMP
C) control gene expression
D) regulate the synthesis of lipids in the cytoplasm
49
49) At puberty, an adolescent female body changes in both structure and function of several organ systems, primarily nether the influence of changing concentrations of estrogens and other steroid hormones. How can one hormone, such as estrogen, mediate then many effects?
A) Estrogen is produced in very big concentration past most every tissue of the trunk.
B) Each cell responds in the same way when steroids bind to the cell surface.
C) Estrogen is kept away from the surface of whatever cells non able to bind it at the surface.
D) Estrogen binds to specific receptors inside many kinds of cells, each with different responses.
fifty
50) Scaffolding proteins are _____.
A) microtubular poly peptide arrays that allow lipid-soluble hormones to get from the cell membrane to the nuclear pores
B) large molecules to which several relay proteins attach to facilitate pour effects
C) relay proteins that orient receptors and their ligands in appropriate directions to facilitate their complexing
D) proteins that can attain into the nucleus of a prison cell to affect transcription
51
51) Phosphorylation cascades involving a series of protein kinases are useful for cellular signal transduction because they _____.
A) are species specific
B) always pb to the aforementioned cellular response
C) amplify the original point many times
D) counter the harmful effects of phosphatases
52
52) GTPase activity is important in the regulation of signal transduction because it _____.
A) increases the available concentration of phosphate
B) decreases the amount of M poly peptide in the membrane
C) hydrolyzes GTP to GDP, thus shutting downwardly the pathway
D) converts cGMP to GTP
53
53) Why has C. elegans proven to be a useful model for understanding apoptosis?
A) The animal does not naturally use apoptosis, simply tin can be induced to do so in the laboratory.
B) The nematode undergoes a fixed and easy-to-visualize number of apoptotic events during its normal development.
C) This plant has a long-studied crumbling machinery that has made agreement its death just a last phase.
D) While the organism ages, its cells die progressively until the whole organism is dead.
54
54) Which of the following describes the events of apoptosis?
A) The cell dies, it is lysed, its organelles are phagocytized, and its contents are recycled.
B) The prison cell'southward DNA and organelles go fragmented, the jail cell dies, and it is phagocytized.
C) The cell's DNA and organelles become fragmented, the cell shrinks and forms blebs, and the jail cell's parts are packaged in vesicles that are digested by specialized cells.
D) The prison cell's nucleus and organelles are lysed, then the cell enlarges and bursts.
55
55) If an adult person has a faulty version of the human analog to ced-4 of the nematode, which of the following is near likely to result?
A) activation of a developmental pathway found in the worm only not in humans
B) a form of cancer in which there is insufficient apoptosis
C) formation of molecular pores in the mitochondrial outer membrane
D) excess skin loss
56
56) Why is apoptosis potentially threatening to the healthy "neighbors" of a dying cell?
A) Prison cell death would unremarkably spread from i cell to the next via paracrine signals.
B) Lysosomal enzymes exiting the dying cell would damage surrounding cells.
C) $.25 of membrane from the dying cell could merge with neighboring cells and bring in foreign receptors.
D) Neighboring cells would activate immunological responses.
57
57) In the nematode C. elegans, ced-9 prevents apoptosis in a normal cell in which of the following ways?
A) It prevents the caspase activeness of ced-3 and ced-iv.
B) Ced-9 remains inactive until it is signaled by ced-3 and other caspases.
C) Ced-ix cleaves to produce ced-three and ced-4.
D) Ced-nine prevents blebbing past its activeness on the cell membrane.
58
58) In research on aging (both cellular aging and organismal crumbling), it has been found that aged cells practice not progress through the cell cycle equally they had previously. Which of the post-obit, if found in cells or organisms as they historic period, would provide show that this is related to cell signaling?
A) Growth factor ligands do not bind as efficiently to receptors.
B) Hormone concentrations decrease.
C) cAMP levels change very frequently.
D) Enzymatic activity declines.
59
59) Apoptosis involves all but which of the following?
A) fragmentation of the DNA
B) activation of cellular enzymes
C) lysis of the cell
D) digestion of cellular contents past scavenger cells
sixty
threescore)A steroid hormone, like estrogen, passes through the plasma membrane and binds to an intracellular protein as shown in the diagram beneath. This activates a bespeak-transduction pathway which results in an increased product of a specific protein.
Which of the post-obit statements would explain what would occur every bit a result of the indicate pathway represented past the diagram?
A) Transfer RNA (t-RNA) would accrue in loftier levels because it is not required for poly peptide synthesis.
B) Ribosomal RNA (r-RNA) levels would increment considering ribosomes are specific for the messenger RNA (m-RNA) with which they bind during transcription of the polypeptide.
C) Dna levels would increase in the nucleus as a effect of the bounden of the hormone-receptor complex with the DNA.
D) Messenger RNA (m-RNA) levels would increase in order to be translated into the protein required past the prison cell.
61
61) Which of the post-obit poses the best evidence that cell-signaling pathways evolved early in the history of life?
A) Cell-signaling pathways are seen in "primitive" cells such as bacteria and yeast.
B) Bacteria and yeast cells signal each other in a process chosen quorum sensing.
C) Point transduction molecules identified in distantly related organisms are similar.
D) Well-nigh signals in all types of cells are received by jail cell surface receptors.
62
62) Cells that are infected, damaged, or accept reached the end of their functional life span often undergo "programmed cell death." This controlled cell suicide is called apoptosis. Select the appropriate clarification of this issue on a cell's life cycle.
A) Apoptosis is regulated by cell surface receptors that signal when a cell has reached its density-dependent limits.
B) During apoptosis, dying cells leak out their contents including digestive enzymes that too destroy healthy cells.
C) During apoptosis, cellular agents chop upward the DNA and fragment the organelles and other cytoplasmic components of a cell.
D) Each cell organelle has poly peptide signals that initiate the breakdown of the organelle'southward components which leads to cell expiry.
Source: https://www.easynotecards.com/notecard_set/61976
0 Response to "Chapter 11 Campbell Biology Reading Guide Quizlet"
Post a Comment